| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
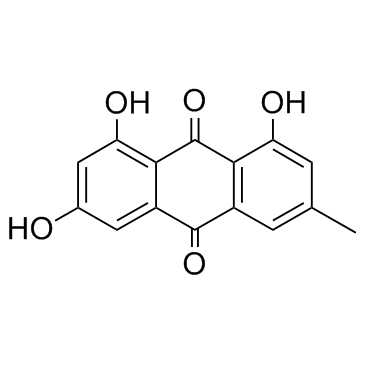 |
Emodin
CAS:518-82-1 |