| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
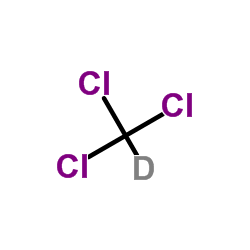 |
chloroform-d
CAS:865-49-6 |
|
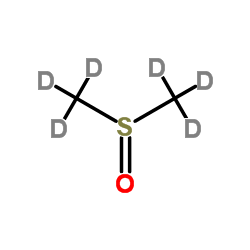 |
DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE-D6
CAS:2206-27-1 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
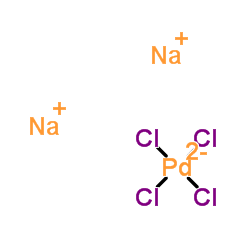 |
Sodium tetrachloropalladate(2-)
CAS:13820-53-6 |
|
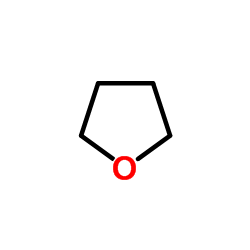 |
thf
CAS:109-99-9 |