| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium carbonate
CAS:497-19-8 |
|
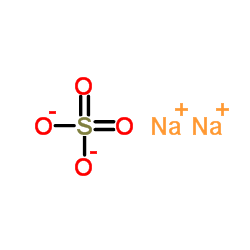 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
sodium persulfate
CAS:7775-27-1 |
|
 |
Hydrogen iodide
CAS:10034-85-2 |
|
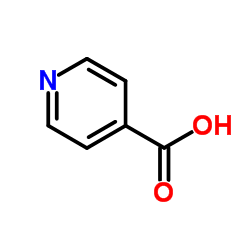 |
Isonicotinic acid
CAS:55-22-1 |