| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
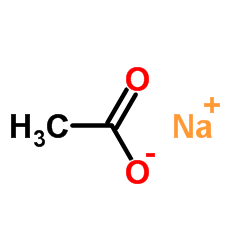 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
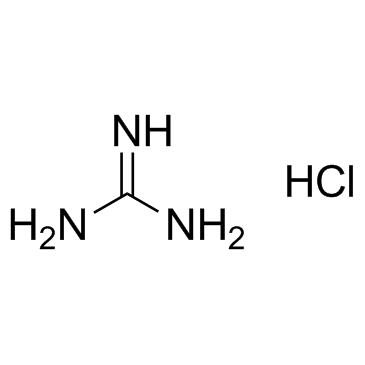 |
Guanidine hydrochloride
CAS:50-01-1 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
 |
potassium chloride
CAS:7447-40-7 |
|
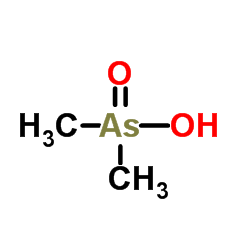 |
Cacodylic acid
CAS:75-60-5 |