| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
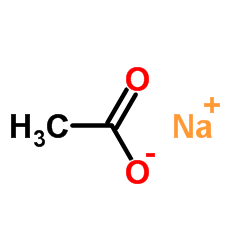 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
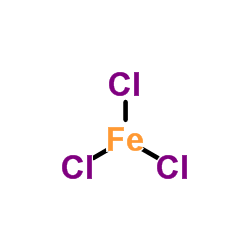 |
Ferric chloride
CAS:7705-08-0 |
|
 |
3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane
CAS:919-30-2 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
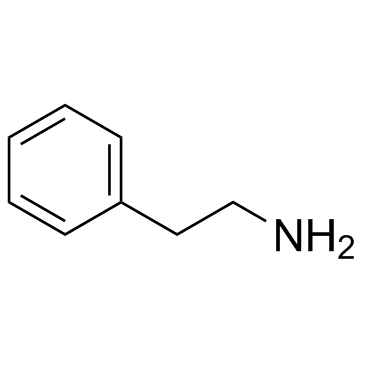 |
2-Phenylethanamine
CAS:64-04-0 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
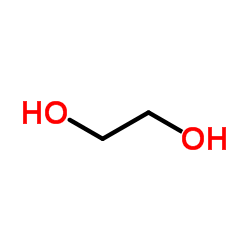 |
Ethylene glycol
CAS:107-21-1 |