| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
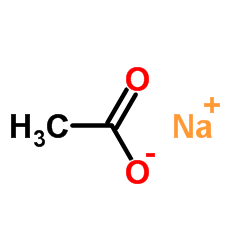 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
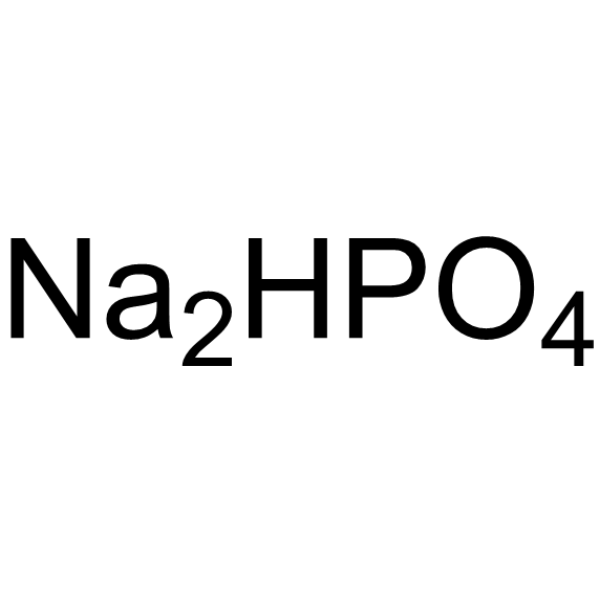 |
Disodium hydrogenorthophosphate
CAS:7558-79-4 |
|
 |
Hydrogen iodide
CAS:10034-85-2 |
|
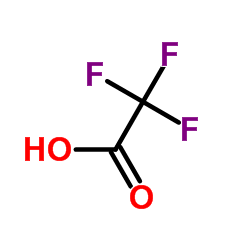 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |