| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Diphenyliodonium hexafluorophosphate
CAS:58109-40-3 |
|
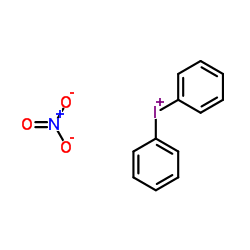 |
Diphenyliodonium nitrate
CAS:722-56-5 |
|
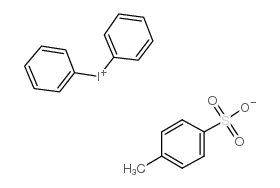 |
Iodonium, diphenyl-, 4-methylbenzenesulfonate (9CI)
CAS:6293-66-9 |