| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethidium bromide
CAS:1239-45-8 |
|
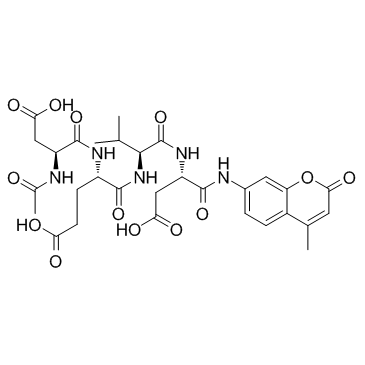 |
Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-AMC ammonium salt
CAS:169332-61-0 |
|
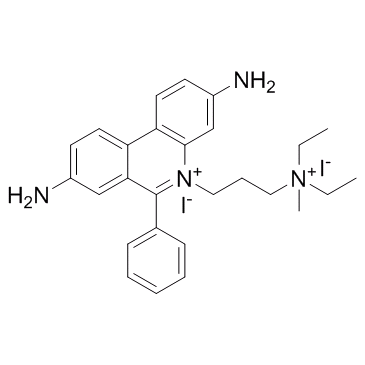 |
Propidium Iodide
CAS:25535-16-4 |