| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
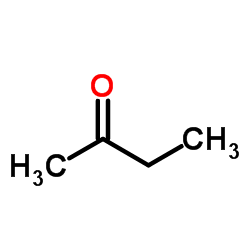 |
2-Butanone
CAS:78-93-3 |
|
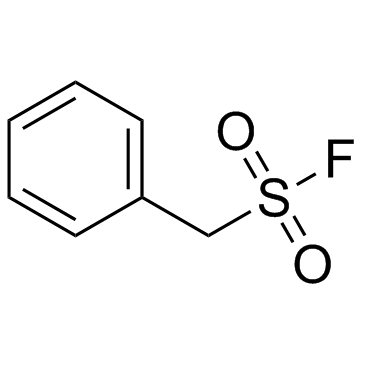 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
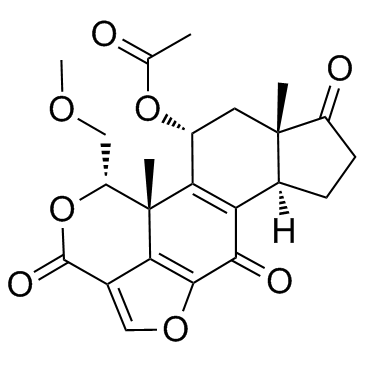 |
Wortmannin
CAS:19545-26-7 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |