| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
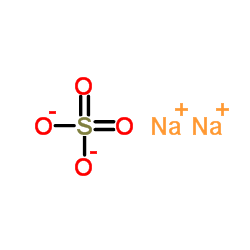 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
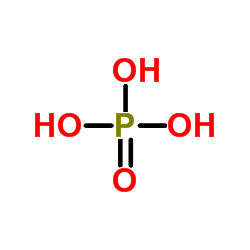 |
Phosphoric acid
CAS:7664-38-2 |
|
 |
Tin(II) chloride
CAS:7772-99-8 |
|
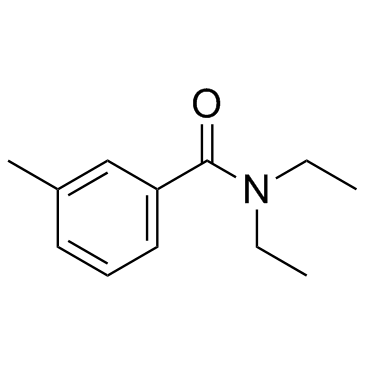 |
N,N-Diethyl-3-methylbenzamide
CAS:134-62-3 |