| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
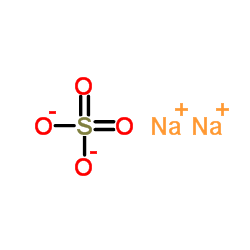 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
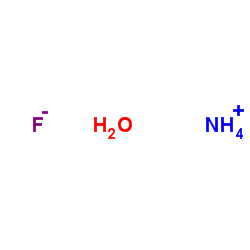 |
Ammonium fluoride
CAS:12125-01-8 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
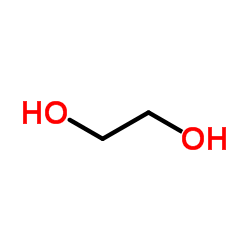 |
Ethylene glycol
CAS:107-21-1 |
|
 |
Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate
CAS:7782-63-0 |