| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Ethanoic anhydride
CAS:108-24-7 |
|
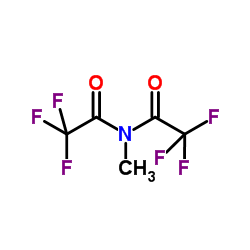 |
N-Methyl-bis(trifluoroacetamide)
CAS:685-27-8 |
|
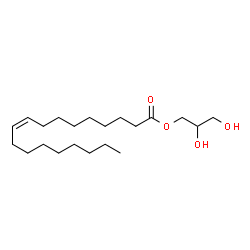 |
Monoolein
CAS:111-03-5 |
|
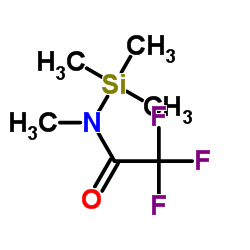 |
MSTFA
CAS:24589-78-4 |
|
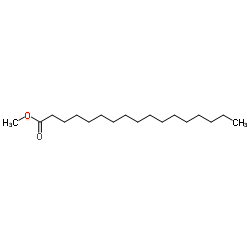 |
Methyl heptadecanoate
CAS:1731-92-6 |