| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
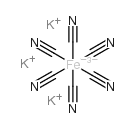 |
Potassium ferricyanide
CAS:13746-66-2 |
|
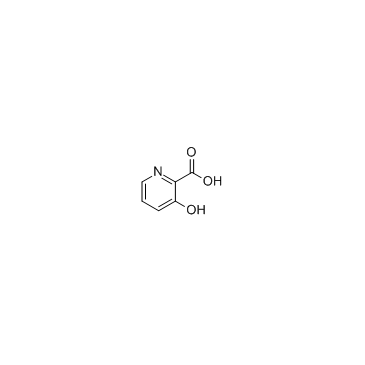 |
3-Hydroxypicolinic acid
CAS:874-24-8 |
|
 |
Potassium
CAS:7440-09-7 |
|
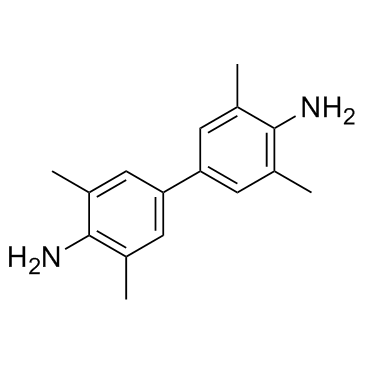 |
Tetramethylbenzidine
CAS:54827-17-7 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
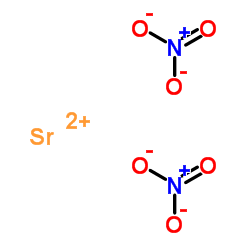 |
Strontium nitrate
CAS:10042-76-9 |
|
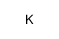 |
potassium hydride
CAS:7693-26-7 |