| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
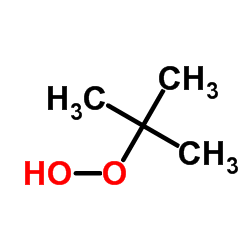 |
tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide
CAS:75-91-2 |
|
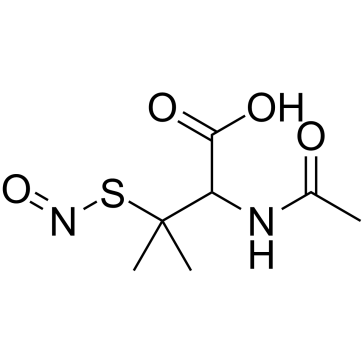 |
N-Acetyl-3-(nitrososulfanyl)valine
CAS:67776-06-1 |
|
 |
Dihydrorhodamine 123
CAS:109244-58-8 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
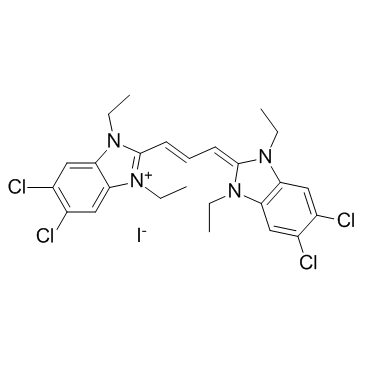 |
JC-1
CAS:3520-43-2 |
|
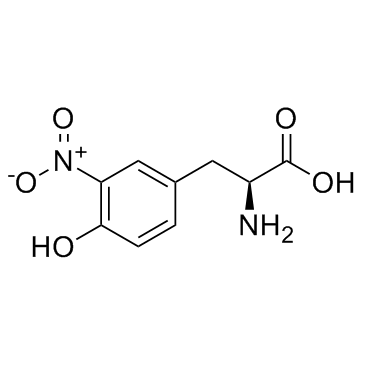 |
3-nitro-L-tyrosine
CAS:621-44-3 |