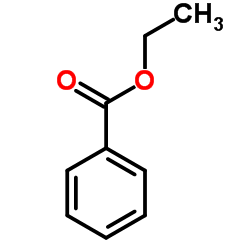
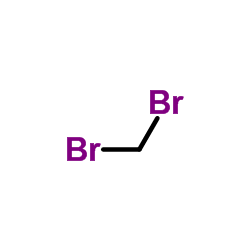
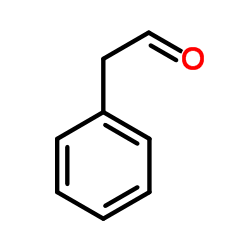
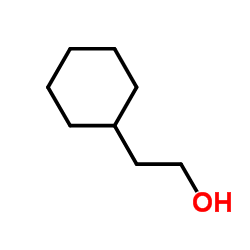
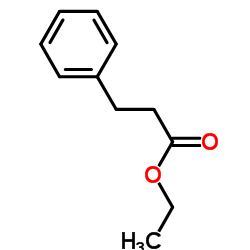
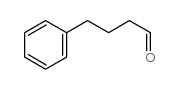
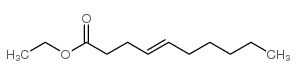
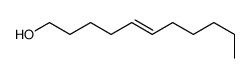
|
~% |
|
~% |
|
~% |
|
~% |
|
~% |