Ethylene versus ethane: A DFT-based selectivity descriptor for efficient catalyst screening
Lang Xu, Eric E. Stangland, Manos Mavrikakis
Index: 10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.019
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
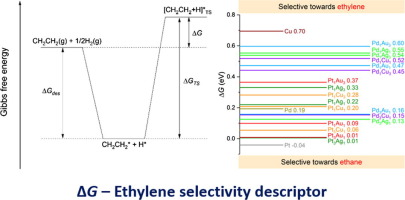
The production of ethylene without its hydrogenation to ethane is a challenge for several catalytic processes. Here, we present a catalyst screening scheme, where the Gibbs free energy difference between the ethylene hydrogenation barrier and ethylene desorption energy is defined as a descriptor for ethylene selectivity. Using plane-wave, dispersion-corrected DFT calculations, we evaluated the descriptor values over the (111) facets of Pt, Pd, and Cu as well as a series of Pt- and Pd-based bimetallic alloys. Our predicted descriptor values indicate that the addition of a Group IB metal (Cu, Ag, or Au) to Pt or Pd improves ethylene selectivity. Ag induces the most significant improvement at 50% while Au has the strongest effect at 75% atomic composition. Pd-based alloys exhibit superior ethylene selectivity over their Pt-based counterparts. Our descriptor model offers an efficient method for the initial screening of catalysts with improved ethylene selectivity.
|
Combined quantitative FTIR and online GC study of Fischer-Tr...
2018-04-06 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.026] |
|
Mechanistic insight into cobalt-catalyzed stereodivergent se...
2018-04-06 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.016] |
|
Principles determining the activity of magnetic oxides for e...
2018-03-30 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.012] |
|
Synthesis and characterization of Ag@Carbon core-shell spher...
2018-03-30 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.02.029] |
|
Mechanistic investigations into the cyclopropanation of elec...
2018-03-30 [10.1016/j.jcat.2018.02.013] |