Vancomycin-modified silica: Synthesis, controlled release and biological activity of the drug.
Joanna Kurczewska, Paulina Sawicka, Magdalena Ratajczak, Marzena Gajęcka, Grzegorz Schroeder
文献索引:Int. J. Pharm. 486 , 226-31, (2015)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Vancomycin was immobilized on three different organically functionalized silicas. The materials obtained were used for a controlled release of the antibiotic. The influence of the type of chemical bond on the in vitro drug release was investigated. A weak ionic bonding caused burst release of the drug within one day. A covalent bonding resulted in a slowdown in the release process and uniformity of dosage release. For these two carriers, biological activity of the drug was retained because the minimal inhibitory concentration values against the strains tested were similar to that of a free form of the drug (about 2 μg/mL). A strong ionic bonding of vancomycin adversely affected both the drug release, as well as its biological activity. A strong base on the surface of the silica prevented disconnection of the antibiotic which then became ineffective.Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
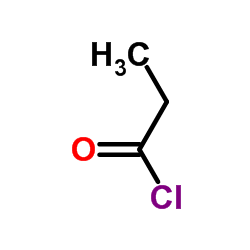 |
丙酰氯
CAS:79-03-8 |
C3H5ClO |
|
Remarkably regioselective deacylation of cellulose esters us...
2014-10-13 [Carbohydr. Polym. 111 , 25-32, (2014)] |
|
Use of multivariate statistical techniques to optimize the s...
2015-03-01 [Talanta 134 , 256-63, (2015)] |
|
Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of carvacrol propio...
2014-10-01 [Inflammation 37(5) , 1575-87, (2014)] |
|
Pyrazolone incorporating bipyridyl metallointercalators as e...
2015-10-05 [Chem. Biol. Interact. 240 , 250-66, (2015)] |
|
(-)-N-[(11)C]propyl-norapomorphine: a positron-labeled dopam...
2000-08-01 [Nucl. Med. Biol. 27(6) , 533-9, (2000)] |