Human primary visual cortex topography imaged via positron tomography.
E L Schwartz, D R Christman, A P Wolf
文献索引:Brain Res. 294(2) , 225-30, (1984)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The visuotopic structure of primary visual cortex was studied in a group of 7 human volunteers using positron emission transaxial tomography (PETT) and 18F-labeled 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose ( [18F]DG). A computer animation was constructed with a spatial structure which was matched to estimates of human cortical magnification factor and to striate cortex stimulus preferences. A lateralized cortical 'checker-board' pattern of [18F]DG was stimulated in primary visual cortex by having subjects view this computer animation following i.v. injection of [18F]DG. The spatial structure of the stimulus was designed to produce an easily recognizable 'signature' in a series of 9 serial PETT scans obtained from each of a group of 7 volunteers. The predicted lateralized topographic 'signature' was observed in 6 of 7 subjects. Applications of this method for further PETT studies of human visual cortex are discussed.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
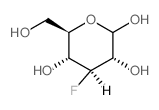 |
3-氟-3-脱氧-D-葡萄糖
CAS:14049-03-7 |
C6H11FO5 |
|
The 1.6 Å crystal structure of pyranose dehydrogenase from A...
2013-01-01 [PLoS ONE 8(1) , e53567, (2013)] |
|
Metabolic pathway of 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose and 2-deoxy-...
1988-03-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 36(3) , 1194-7, (1988)] |
|
Noninvasive demonstration of in vivo 3-fluoro-3-deoxy-D-gluc...
1987-08-01 [J. Neurochem. 49(2) , 428-33, (1987)] |
|
31P and 3-fluoro-3-deoxy-D-glucose 19F in vivo NMR spectrosc...
1991-02-01 [NMR Biomed. 4(1) , 38-40, (1991)] |
|
An expedient enzymatic route to isomeric 2-, 3- and 6-monode...
2012-09-01 [Carbohydr. Res. 358 , 12-8, (2012)] |