Inactivation of Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigote forms in blood components with a Psoralen and Ultraviolet A light.
P Gottlieb, H Margolis-Nunno, R Robinson, L G Shen, E Chimezie, B Horowitz, E Ben-Hur
文献索引:Photochem. Photobiol. 63(5) , 562-5, (1996)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Inactivation of the blood-borne parasite Trypanosoma cruzi by UVA and 4'-aminomethyl-4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen (AMT) was studied in the blood components fresh frozen plasma (FFP) and platelet concentrate (PC). The AMT was utilized at a concentration of 50 micrograms/mL and the inactivation procedure included the flavonoid rutin (at 0.35 mM), a quencher of type I and type photo-reactants, which we have previously found to maintain platelet integrity during this treatment regimen. Within both FFP and PC, complete inactivation of the infective form of T. cruzi, the trypomastigote, was achieved at a UVA (320-400 nm radiation) fluence of 4.2 J/cm2. We note that while the infectivity of the parasite is eliminated at 4.2 J/cm2 the trypomastigote motility continues for at least 16 h-post-treatment and is inhibited only after much higher light doses. Isolation of total DNA from the parasite cells after treatment in the presence of 3H-AMT indicated that at the lethal UVA influence about 0.5 AMT adducts per kilobase pairs occurred. These results suggest that this psoralen plus UVA methodology which shows promise in enhancing the viral safety of PC, may in addition eliminate bloodborne T. cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
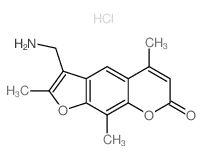 |
4′-氨甲基三唑仑盐酸盐
CAS:62442-61-9 |
C15H16ClNO3 |
|
In vivo footprint of a picornavirus internal ribosome entry ...
2007-11-01 [J. Gen. Virol. 88(Pt 11) , 3053-62, (2007)] |
|
'RNA walk' a novel approach to study RNA-RNA interactions be...
2010-01-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 38(1) , e5, (2010)] |
|
Psoralen preparation of antigenically intact noninfectious r...
1992-07-01 [J. Virol. Methods 38(1) , 93-102, (1992)] |
|
Yeast U1 snRNP-pre-mRNA complex formation without U1snRNA-pr...
2001-01-01 [RNA 7(1) , 133-42, (2001)] |
|
Quencher-enhanced specificity of psoralen-photosensitized vi...
1994-09-01 [Transfusion 34(9) , 802-10, (1994)] |