Dietary zerumbone prevents against ultraviolet B-induced cataractogenesis in the mouse.
Bo-Yie Chen, David Pei-Cheng Lin, Kuo-Chen Su, Yi-Ling Chen, Chia-Yung Wu, Mei-Ching Teng, Yuan-Ting Tsai, Chi-Yun Sun, Soo-Ray Wang, Han-Hsin Chang
文献索引:Mol. Vis. 17 , 723-30, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
To investigate the preventive effect of dietary zerumbone against UVB-induced cataractogenesis.A total of 50 six-week-old female ICR mice were split into five groups (each contained 10 mice) and exposed to UVB (0.72 J/cm(2)/daily) at noon for 7 days, except for the blank control group. The mice with UVB exposure were fed with zerumbone as a dietary supplement at 0, 1, 10, and 100 mg/kg of bodyweight, respectively, starting from one day before UVB exposure. On day 7, at 4 h after UVB exposure, all mice were subjected to cataract examination and lens opacity scoring, in correlation with levels of MDA (malondialdehyde), GSH (glutathione), GR (GSH reductase), GPx (glutathione peroxidase), and SOD (superoxide dismutase) in the lens.Dietary zerumbone at 100 mg/kg after UVB exposure was effective in decreasing lens opacity scores (p<0.001) and to reduce MDA (p<0.001), while GSH and GR levels were significantly increased (both p<0.001) in the lens. SOD was also increased with dietary zerumbone at 100 mg/kg (p=0.115), whereas GPx (p=0.171) levels were lower as compared with those without zerumbone after UVB exposure.These results suggest that zerumbone may protect against UVB-induced cataractogensis through reducing lipid peroxides and enhancing the endogenous antioxidant GSH level and GR activity.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
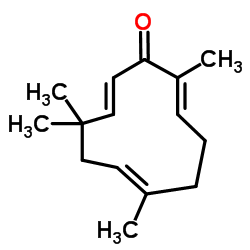 |
花姜酮
CAS:471-05-6 |
C15H22O |
|
Zingiber zerumbet CYP71BA1 catalyzes the conversion of α-hum...
2011-03-01 [Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68(6) , 1033-40, (2011)] |
|
Altered cross-linking of HSP27 by zerumbone as a novel strat...
2011-03-15 [Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 79(4) , 1196-205, (2011)] |
|
Effects of selected food phytochemicals in reducing the toxi...
2010-12-01 [Arch. Toxicol. 84(12) , 957-66, (2010)] |
|
Ginger phytochemicals mitigate the obesogenic effects of a h...
2011-09-01 [Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 55 Suppl 2 , S203-13, (2011)] |
|
Anti-inflammatory effect of zerumbone on acute and chronic i...
2010-10-01 [Fitoterapia 81(7) , 855-8, (2010)] |