Selenoxidation by flavin-containing monooxygenases as a novel pathway for beta-elimination of selenocysteine Se-conjugates.
M Rooseboom, J N Commandeur, G C Floor, A E Rettie, N P Vermeulen
文献索引:Chem. Res. Toxicol. 14(1) , 127-34, (2001)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Previously, it was shown that beta-elimination of selenocysteine Se-conjugates by rat renal cytosol leading to pyruvate formation was not solely catalyzed by pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzymes. It was hypothesized that selenoxidation of the selenocysteine Se-conjugates, followed by syn-elimination, may be an alternative mechanism for pyruvate formation. In this study, selenoxidation of selenocysteine Se-conjugates was studied using rat liver microsomes and recombinant human oxidative enzymes. For all six selenocysteine Se-conjugates that were tested, it was found that rat liver microsomal incubations led to the formation of pyruvate, whereas the corresponding selenoxides were not observed. Microsomal pyruvate formation from Se-benzyl-L-selenocysteine (SeBC) was NADPH-dependent, but only marginally inhibited by several P450 inhibitors. Inhibition by methimazole and by heat pretreatment and stimulation by n-octylamine indicated that flavin-containing monooxygenases are mainly responsible for pyruvate formation from the selenocysteine Se-conjugates in rat liver microsomes. In the case of S-benzyl-L-cysteine, the sulfur analogue of SeBC, pyruvate formation was not observed. For this substrate, a chemically stable sulfoxide could be observed, as previously described. By using recombinantly expressed human flavin-containing monooxygenases and P450 enzymes, it was delineated that SeBC is selenoxidized by human FMOs, but not by human P450s. The k(cat)/K(m) of selenoxidation was 3.8-fold higher for FMO-1 than for FMO-3. In conclusion, selenoxidation of selenocysteine Se-conjugates catalyzed by FMOs and subsequently syn-elimination has taken place as an alternative route for the formation of pyruvate from selenocysteine Se-conjugates. Although selenoxides are known to be easily reduced by thiol compounds, microsomal pyruvate formation from SeBC was only 75% inhibited in the presence of an excess of glutathione. This indicates that even in the presence of physiological concentrations of reducing thiol compounds, selenoxides of selenocysteine Se-conjugates may undergo syn-elimination to some extent. Whether selenoxides and/or selenenic acids that are formed are involved in the activity of chemopreventive selenocysteine Se-conjugates remains to be established.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
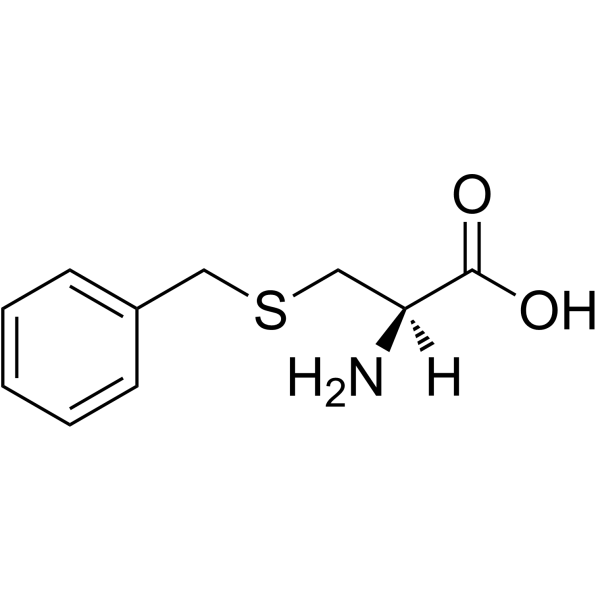 |
S-苄基-L-半胱氨酸
CAS:3054-01-1 |
C10H13NO2S |
|
Comparison of peak-picking workflows for untargeted liquid c...
2015-01-15 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 29(1) , 119-27, (2014)] |
|
Formation of a dehydroalanyl residue from S-benzylcysteine u...
1991-12-01 [Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 38(6) , 601-2, (1991)] |
|
Synthesis and biological evaluation of L-cysteine derivative...
2007-07-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17 , 3921-4, (2007)] |
|
Role of allyl group in the hydroxyl and peroxyl radical scav...
2011-11-17 [J. Phys. Chem. B 115(45) , 13408-17, (2011)] |
|
Localization and capacity of the last step of mercapturic ac...
1991-01-01 [Pflugers Arch. 417(5) , 523-7, (1991)] |