New therapeutic strategy for amino acid medicine: prophylactic and healing promoting effect of monosodium glutamate against NSAID-induced enteropathy.
Kikuko Amagase, Akimu Ochi, Azusa Kojo, Ami Mizunoe, Masaya Taue, Naoya Kinoshita, Eiji Nakamura, Koji Takeuchi
文献索引:J. Pharmacol. Sci. 118(2) , 131-7, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We reviewed the effect of monosodium glutamate (MSG) on the development and healing of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced small intestinal lesions in rats. Loxoprofen (60 mg/kg, p.o.) induced lesions in the small intestine within 24 h, accompanied by a decrease of Muc2 expression and an increase in enterobacterial invasion and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression. These lesions were prevented when MSG was given as a mixture of powdered food for 5 days before the loxoprofen treatment. This effect of MSG was accompanied by an increase in Muc2 expression / mucus secretion as well as the suppression of bacterial invasion and iNOS expression. These intestinal lesions healed spontaneously within 6 days, but the process was impaired by the repeated administration of low-dose loxoprofen (30 mg/kg) for 5 days after the ulceration, with the decrease of vascular endothelial derived growth factor (VEGF) expression and angiogenesis. The healing-impairing effect of loxoprofen was prevented by feeding 5% MSG for 5 days after the ulceration. These results suggest that MSG not only prevents loxoprofen-induced small intestinal damage but also promotes a healing of these lesions; the former is functionally associated with the increase in Muc2 expression / mucus secretion and the suppression of bacterial invasion and iNOS expression, while the latter is associated with the stimulation of VEGF expression/angiogenesis.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
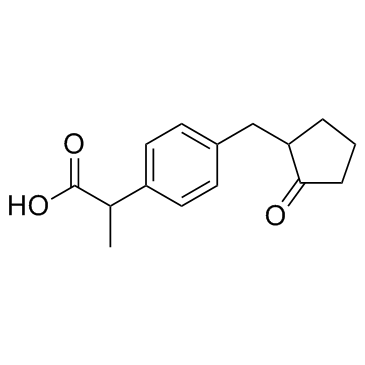 |
洛索洛芬
CAS:68767-14-6 |
C15H18O3 |
|
Determination of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in hum...
2015-09-01 [Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 59 , 364-71, (2015)] |
|
Risk of peptic ulcer bleeding associated with Helicobacter p...
2015-02-01 [J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 30(2) , 292-8, (2015)] |
|
Effect of X-ray exposure on the pharmaceutical quality of dr...
2015-06-01 [Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 41 , 953-8, (2015)] |
|
Influence of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the ant...
2011-01-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 34(2) , 233-7, (2011)] |
|
Protective effect of geranylgeranylacetone against loxoprofe...
2011-02-10 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 652(1-3) , 121-5, (2011)] |