Abnormal adenosine 3'.5'-monophosphate stimulation of renal 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D production in hyp mice: evidence that 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1 alpha-hydroxylase dysfunction results from aberrant intracellular function.
T Nesbitt, G A Davidai, M K Drezner
文献索引:Endocrinology 124(3) , 1184-9, (1989)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Previously we have established that abnormal regulation of renal 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD)-1 alpha-hydroxylase in Hyp mice involves the PTH-adenylate cyclase component of enzyme activation. However, it remains unknown if the muted effects of PTH result from 1) abnormal second messenger production or 2) an intracellular defect limiting enzyme activation. To distinguish between these possibilities, we compared cAMP stimulation of renal 25OHD-1 alpha-hydroxylase in normal, phosphate-depleted normal, and Hyp mice. Administration of N6-monobutyryl cAMP iv (200 mg/kg/day) increased enzyme activity in normal (4.1 +/- 1.7 vs. 40.7 +/- 7.0 fmol/mg kidney.min) and phosphate-depleted mice (13.3 +/- 1.8 vs. 78.2 +/- 10.4) to a level significantly greater than that achieved in Hyp mice (7.4 +/- 1.1 vs. 22.7 +/- 3.6). Moreover, similar to our observations after PTH stimulation, the apparent abnormal cAMP effect did not result from an altered time course of enzyme activation or a rightward shift in the dose response. Collectively, these data indicate that abnormal regulation of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D production in Hyp mice results from aberrant intracellular regulation of 25OHD-1 alpha-hydroxylase, a defect probably related to deranged phosphate transport in the renal tubule.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
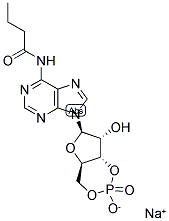 |
N6-丁酰腺苷3′:5′-环一磷酸钠
CAS:70253-67-7 |
C14H17N5NaO7P |
|
Protein kinase A and B-Raf mediate extracellular signal-regu...
2009-11-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 76 , 1123-1129, (2009)] |
|
Cryptic receptors for insulin-like growth factor II in the p...
1996-06-13 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1282(1) , 57-62, (1996)] |
|
Expression of aquaporin 8 and its up-regulation by cyclic ad...
2003-04-01 [Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 188(4) , 997-1001, (2003)] |
|
Acquisition of a transcriptionally permissive state during t...
1992-02-01 [Dev. Biol. 149(2) , 457-62, (1992)] |
|
The insulin-like effect of growth hormone on insulin-like gr...
1990-06-01 [Biochem. J. 268(2) , 353-7, (1990)] |