Glycyl-L-sarcosine absorption across ovine omasal epithelium during coincubation with other peptide substrates and volatile fatty acids.
M Q McCollum, K E Webb
文献索引:J. Anim. Sci. 76(10) , 2706-11, (1998)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
To define the interactions between the absorption of glycyl-L-sarcosine (Gly-Sar; .1 mM) and glycine, L-methionylglycine, glycyl-L-leucine, L-carnosine, or L-methionylglycyl-L-methionyl-L-methionine (each at 5 mM), ovine omasal epithelium was collected from eight wethers (average BW=69+/-8.2 kg) and mounted in parabiotic chambers. [1,2]-[14C]Glycyl-L-sarcosine was used as a marker to monitor the presence of Gly-Sar. The Gly-Sar concentration in the omasal epithelium after 60 min of incubation was greatest (P < .05; .0055 nmol/mg dry tissue) when only Gly-Sar was present. Glycine inhibited (P < .05) Gly-Sar movement through the tissue by 20%, and peptide substrates inhibited (P < .05) Gly-Sar movement by 60 to 85%. The appearance of Gly-Sar in serosal buffers increased quadratically (P < .001) with time. Numerically, Gly-Sar appearance in serosal buffers was stimulated by the presence of glycine and peptide substrates. In a second experiment, ovine omasal epithelium was collected from four lambs (average BW=47+/-6.0 kg) to determine the interactions of Gly-Sar absorption (.1 mM) alone or when coincubated with either 10 mM butyric acid, or with a mixture of VFA (50 mM acetic acid, 40 mM propionic acid, and 10 mM butyric acid). The movement of Gly-Sar through the omasal epithelium was greatest (P < .05) when only Gly-Sar was present, and the VFA mixture inhibited (P < .05) Gly-Sar movement by 84%. Results from these studies support the idea that peptides can be absorbed across omasal epithelium and that the process involves mediated as well as nonmediated mechanisms, including possibly paracellular transport.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
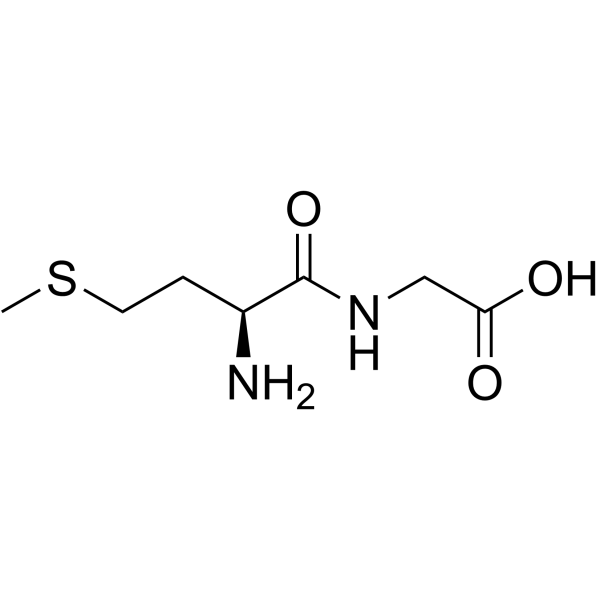 |
L-甲硫氨酰甘氨酸
CAS:14486-03-4 |
C7H14N2O3S |
|
Tissue-engineered cartilage with inducible and tunable immun...
2014-07-01 [Biomaterials 35(22) , 5921-31, (2014)] |
|
A dynamically modified microfluidic poly(dimethylsiloxane) c...
2002-10-01 [Electrophoresis 23(20) , 3558-66, (2002)] |
|
Radical scavenging activities of Tyr-, Trp-, Cys- and Met-Gl...
2016-04-15 [Food Chem. 197 , 807-13, (2015)] |
|
Absorption of L-carnosine, L-methionine, and L-methionylglyc...
1995-11-01 [J. Anim. Sci. 73(11) , 3464-75, (1995)] |
|
Fragmentation chemistry of [Met-Gly]•+, [Gly-Met]•+, and [Me...
2013-04-01 [J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 24(4) , 543-53, (2013)] |