Degradation of 2-chloroallylalcohol by a Pseudomonas sp.
J J van der Waarde, R Kok, D B Janssen
文献索引:Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59(2) , 528-35, (1993)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Three Pseudomonas strains capable of utilizing 2-chloroallylalcohol (2-chloropropenol) as the sole carbon source for growth were isolated from soil. The fastest growth was observed with strain JD2, with a generation time of 3.6 h. Degradation of 2-chloroallylalcohol was accompanied by complete dehalogenation. Chloroallylalcohols that did not support growth were dechlorinated by resting cells; the dechlorination level was highest if an alpha-chlorine substituent was present. Crude extracts of strain JD2 contained inducible alcohol dehydrogenase activity that oxidized mono- and dichloroallylalcohols but not trichloroallylalcohol. The enzyme used phenazine methosulfate as an artificial electron acceptor. Further oxidation yielded 2-chloroacrylic acid. The organism also produced hydrolytic dehalogenases converting 2-chloroacetic acid and 2-chloropropionic acid.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
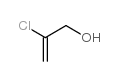 |
2-氯-2-丙烯-1-醇
CAS:5976-47-6 |
C3H5ClO |
|
Kinetic studies of the homogeneous abiotic reactions of seve...
[Appl. Geochem. 13(6) , 779-85, (1998)] |
|
Derivatives of phosphorus acids and 2-chloro-2-propen-1-ol. ...
[Russ. Chem. Bull. 16(6) , 1233-38, (1967)] |
|
Asymmetric synthesis of conformationally constrained fingoli...
2007-12-13 [J. Med. Chem. 50(25) , 6428-35, (2007)] |
|
Photofragment imaging study of the CH2CCH2OH radical interme...
2007-10-21 [J. Chem. Phys. 127(15) , 154316, (2007)] |