Permeation of 6-nitro-3-phenylacetamide benzoic acid (NIPAB) and hydrolysis by penicillin acylase immobilized in emulsion liquid membranes.
I Miesiac, K Schügerl, J Szymanowski
文献索引:J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 55(1) , 1-8, (1992)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The effects of various commercial and model surfactants of different structure and hydrophilicity were studied on water-in-oil (w/o) emulsion stability, potassium cation leakage and permeation of 6-nitro-3-phenylacetamide benzoic acid in a model system using Penicillin acylase (EC 3.5.1.11) immobilized in a liquid membrane. Both emulsion stability, potassium leakage and permeation of organic substances depend upon hydrophilicity of surfactants. Hydrophilic surfactants may be used to stabilize emulsions only in mixtures with hydrophobic emulsifiers. Additions of small quantities of hydrophilic surfactants to the system in which permeation occurs together within an enzymatic process may be advantageous. Both the rate of permeation and potassium transfer significantly increase when hydrophilic surfactants are present. There was no relationship observed between potassium cation transfer from the internal phase and emulsion stability in the storage test.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
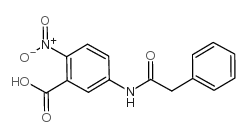 |
3-苯乙酰氨基-6-硝基苯甲酸
CAS:52033-70-2 |
C15H12N2O5 |
|
Improving the diastereoselectivity of penicillin G acylase f...
2012-03-01 [Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 25(3) , 135-44, (2012)] |
|
Preparation and general properties of crystalline penicillin...
1974-01-01 [Hoppe. Seylers. Z. Physiol. Chem. 354 , 45, (1974)] |
|
New active site oriented glyoxyl-agarose derivatives of Esch...
2007-01-01 [BMC Biotechnol. 7 , 54, (2007)] |
|
The role of hydrophobic active-site residues in substrate sp...
2002-04-01 [Eur. J. Biochem. 269(8) , 2093-100, (2002)] |
|
The use of chromogenic reference substrates for the kinetic ...
1999-11-01 [Anal. Biochem. 275(1) , 47-53, (1999)] |