Characterization of liposomes carrying von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha: a potential substitute for platelet transfusion.
T Kitaguchi, M Murata, K Iijima, K Kamide, T Imagawa, Y Ikeda
文献索引:Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 261 , 784-789, (1999)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Platelet glycoprotein (GP) Ib/IX/V complex is a receptor for von Willebrand factor (vWf), which plays a crucial role in primary hemostasis by mediating platelet adhesion to injured blood vessels. We have expressed in CHO cells a fragment of GPIba that retained a vWf-binding function. The recombinant fragment (rGPIba) was incorporated into liposomes and evaluated their functions in vitro. rGPIba on the liposome surface was detectable by flow cytometric analysis. Addition of vWf and ristocetin caused specific agglutination of rGPIbalpha-liposomes, as evaluated by an aggregometer or a fluorescent microscopy. When ristocetin was added to platelet-rich plasma (PRP) pre-mixed with rhodamine-labeled rGPIbalpha-liposomes, platelets aggregated and rhodamine-fluorescence was strongly positive in the platelet thrombi, suggesting that heterologous aggregation (attachment of liposomes to platelets) occurred. Platelet aggregation in PRP at low platelet concentration (20-80 x 10(6)/ml) was enhanced by rGPIbalpha-liposomes in a dose-dependent manner. Thus, rGPIbalpha-liposomes may accumulate on vWf-exposed subendothelial tissues and enhance platelet function in vivo, supporting hemostasis in thrombocytopenic individuals.Copyright 1999 Academic Press.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
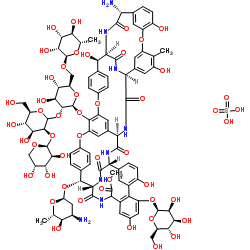 |
硫酸瑞斯托菌素A
CAS:11140-99-1 |
C95H110N8O44.H2SO4 |
|
Overproduction of Ristomycin A by activation of a silent gen...
2014-10-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58(10) , 6185-96, (2014)] |
|
Jordan, D.C., D. Gottlieb and P. Shaw,, ed.
[Antibiotics New York , (1967) 1 , 84] |
|
Ristocetin- and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation at phy...
1998-09-01 [Thromb. Haemost. 80 , 428-436, (1998)] |
|
Elevated plasma glycocalicin levels and decreased ristocetin...
1998-07-01 [Am. J. Kidney Dis. 32 , 132-138, (1998)] |