Inhibition of cytokine-inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat microglia and murine macrophages by methyl-2,5-dihydroxycinnamate.
J Zielasek, B Müller, H P Hartung
文献索引:Neurochem. Int. 29(1) , 83-7, (1996)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Microglial cells are resident macrophages in the central nervous system (CNS) which serve specific functions in the defence of the CNS against microorganisms, the removal of tissue debris in neurodegenerative diseases or during normal development, and in autoimmune inflammatory disorders of the brain. Microglia express a cytokine-inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase, which leads to the production of nitric oxide (NO). Since NO is highly toxic to neurons and oligodendrocytes, we were interested to test down-regulating neuropeptides and second messenger de-activators in order to identify novel antagonists of cytokine-induced NO production. We found that only the tyrosine kinase inhibitor methyl-2,5-dihydroxycinnamate suppressed cytokine-induced NO production by rat microglial cells and murine macrophages, while a range of other tyrosine kinase inhibitors, neuropeptides and growth factors was ineffective. Since NO production may play a role in the pathogenesis of experimental neuro-immunological disorders like experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and experimental autoimmune neuritis, our findings suggest a possible therapeutic role for tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
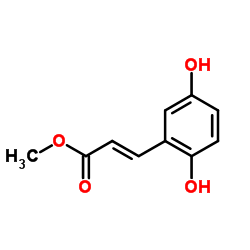 |
2,5-二羟基肉桂酸甲酯
CAS:63177-57-1 |
C10H10O4 |
|
Direct inhibition of the hexose transporter GLUT1 by tyrosin...
2001-01-23 [Biochemistry 40(3) , 777-90, (2001)] |
|
Mechanism of topoisomerase II inhibition by staurosporine an...
1996-10-18 [J. Biol. Chem. 271(42) , 26418-23, (1996)] |
|
Signal pathways that transduce growth factor-stimulated mito...
1998-07-01 [Bone 23(1) , 17-26, (1998)] |
|
Suppression of tyrosine kinase activity inhibits [3H]thymidi...
1997-07-01 [J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82(7) , 2143-7, (1997)] |
|
Regulation of the renal Na-HCO3 cotransporter: IX. Modulatio...
1998-10-16 [Regul. Pept. 77(1-3) , 155-61, (1998)] |