Formation of a novel 20-hydroxylated metabolite of lipoxin A4 by human neutrophil microsomes.
H Sumimoto, R Isobe, Y Mizukami, S Minakami
文献索引:FEBS Lett. 315(3) , 205-10, (1993)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Lipoxin A4 (LXA4) is a biologically active compound produced from arachidonic acid via interactions of lipoxygenases. Incubation of LXA4 either with human neutrophils or with the neutrophil microsomes leads to formation of a polar compound on a reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. We have identified the metabolite as 20-hydroxy-LXA4, a novel metabolite of arachidonic acid, on the basis of ultraviolet spectrometry and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The LXA4 omega-hydroxylation requires both molecular oxygen and NADPH, and is inhibited by carbon monoxide, by antibodies raised against NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase, or competitively by leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and LTB5, substrates of LTB4 omega-hydroxylase. These findings indicate that the formation of 20-hydroxy-LXA4 is catalyzed by a neutrophil cytochrome P-450, the LTB4 omega-hydroxylase.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
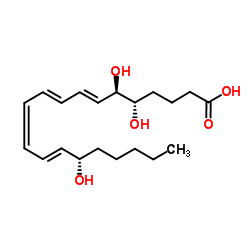 |
Lipoxin A4
CAS:89663-86-5 |
C20H32O5 |
|
HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome.
2009-01-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database issue) , D603-10, (2009)] |
|
The human serum metabolome.
2011-01-01 [PLoS ONE 6(2) , e16957, (2011)] |
|
Protective effects of n-6 fatty acids-enriched diet on intes...
2015-02-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 172(3) , 910-23, (2015)] |
|
In Vivo Availability of Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators in Oxa...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0143141, (2015)] |
|
Lipidomics reveals a remarkable diversity of lipids in human...
2010-11-01 [J. Lipid Res. 51(11) , 3299-305, (2010)] |