Induction of neutrophilic differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemic cells by branched-chain carboxylic acid anticonvulsant drugs.
S A Fischkoff, E Walter
文献索引:J. Biol. Response Mod. 3(2) , 132-7, (1984)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The anticonvulsant drug 1-methyl-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid ( MCCA ) has been shown to cause maturation of murine neuroblastoma cells in vitro at concentrations that are pharmacologically achievable. HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cells cultured with this drug underwent a dose-dependent decrease in growth. Similarly, neutrophilic differentiation, based on morphologic criteria and the acquisition of the ability to reduce nitroblue tetrazolium and phagocytose yeast, was observed. Valproic acid, a clinically available anticonvulsant that is chemically related to MCCA , likewise inhibited growth and promoted maturation of HL-60 cells, although only at concentrations above the recommended therapeutic blood levels. MCCA was additive in its ability to induce differentiation of HL-60 with retinoic acid, another compound that induces differentiation at pharmacologic concentrations. MCCA , or similar branched-chain fatty acids, may be useful in the treatment of human leukemia, particularly in combination with other differentiation-inducing drugs.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
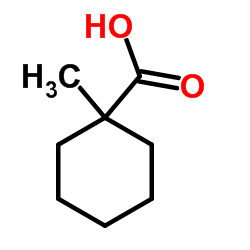 |
1-甲基-1-环己甲酸
CAS:1123-25-7 |
C8H14O2 |
|
Human CYP2C9 and CYP2A6 mediate formation of the hepatotoxin...
1997-11-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283(2) , 698-703, (1997)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of valproate analogs i...
1993-05-01 [Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 14(4) , 325-39, (1993)] |
|
[A method for determining arsenic in biological material].
1992-01-01 [Sud. Med. Ekspert. 35(1) , 31-2, (1992)] |
|
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of valproate analogues...
1994-01-01 [Epilepsia 35(1) , 234-43, (1994)] |
|
Regulation of c- and N-myc expression during induced differe...
1991-04-01 [Oncogene 6(4) , 633-8, (1991)] |