| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
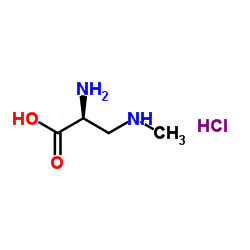 |
3-(甲氨基)-L-丙氨酸盐酸盐
CAS:16012-55-8 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
3-(甲氨基)-L-丙氨酸盐酸盐
CAS:16012-55-8 |