Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry
1985-01-01
Comparison of the effects of amphetamine and a fluorinated analogue on locomotion and exploratory activity in the mouse.
R E Dubin, R J Reiffenstein, G B Baker, R T Coutts, A Benderly
文献索引:Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 9(5-6) , 681-5, (1985)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
(+)-Amphetamine (AM) and its fluorinated analogue (+)-2-amino-3-fluoro-1-phenylpropane (fluoroamphetamine, FAM) were compared with regard to their effects on locomotor and exploratory activity in mice. Both drugs caused a reduction in spontaneous exploration, but this effect was more marked with FAM than with AM at 1 h after injection. Both compounds increased locomotor activity 10 min after injection, but FAM had sedative effects after 1 h, while AM continued to be stimulatory.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
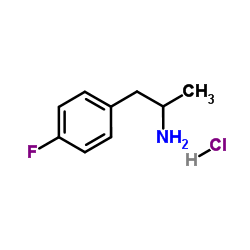 |
4-氟-α-甲基苯乙胺盐酸盐
CAS:64609-06-9 |
C9H13ClFN |
相关文献:
更多...
|
Detection of the synthetic drug 4-fluoroamphetamine (4-FA) i...
2012-02-10 [Forensic Sci. Int. 215(1-3) , 3-7, (2012)] |
|
Isomers of fluoroamphetamines detected in forensic cases in ...
2012-07-01 [Int. J. Legal Med. 126(4) , 541-7, (2012)] |
|
Cardiogenic shock after use of fluoroamphetamine confirmed w...
2014-12-01 [Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 52(10) , 1292-5, (2014)] |
|
Fenfluramine, p-chloroamphetamine and p-fluoroamphetamine st...
1984-03-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 228(3) , 593-9, (1984)] |
|
Tissue levels and some in vivo responses to a monofluorinate...
1986-12-15 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 35(24) , 4423-9, (1986)] |