Biocatalytic resolution of glycidyl phenyl ether using a novel epoxide hydrolase from a marine bacterium,Rhodobacterales bacteriumHTCC2654
Jung-Hee Woo, Ji-Hyun Kang, Young-Ok Hwang, Jang-Cheon Cho, Sang-Jin Kim, Sung Gyun Kang, Jung-Hee Woo, Ji-Hyun Kang, Young-Ok Hwang, Jang-Cheon Cho, Sang-Jin Kim, Sung Gyun Kang
文献索引:J. Biosci. Bioeng. 109(6) , 539-44, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
As a continuous effort of developing highly enantioselective epoxide hydrolase from marine microorganisms, it was found that Rhodobacterales bacterium HTCC2654 was highly enantioselective toward racemic glycidyl phenyl ether (GPE). An open reading frame (ORF) encoding a putative epoxide hydrolase (EHase) was cloned from the genome of R. bacterium HTCC2654, followed by expression and purification in Escherichia coli. The purified EHase (REH) hydrolyzed ( S)-GPE preferentially over ( R)-GPE. Enantiopure ( R)-GPE from kinetic resolution of 29.2 mM racemic GPE using the purified REH could be obtained with enantiopurity of more than 99.9% enantiomeric excess (ee) and 38.4% yield (theoretical, 50%) within 20 min (enantiomeric ratio ( E-value): 38.4). The enantioselective activity of REH toward GPE was also confirmed by the analysis of the vicinal diol, 3-phenoxy-1,2-propanediol. To our knowledge, this study demonstrates the highest enantioselective resolution of racemic GPE using a purified biocatalyst among the known native EHases.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
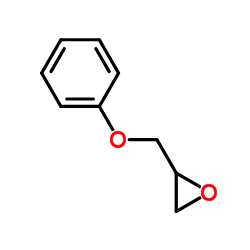 |
环氧丙基苯基醚
CAS:122-60-1 |
C9H10O2 |
|
First multi-reactive dextran-based inisurf for atom transfer...
2015-10-05 [Carbohydr. Polym. 130 , 141-8, (2015)] |
|
Synthesis, biological evaluation and mechanistic studies of ...
2012-01-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20 , 893-902, (2012)] |
|
Interfacial kinetics of a model epoxy-amine addition reactio...
2012-10-21 [Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(39) , 13532-4, (2012)] |
|
Stereoselective epoxidation of phenyl allyl ether by alkene-...
1992-04-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37(1) , 28-31, (1992)] |
|
The use of laboratory methods in contact dermatitis induced ...
1990-05-01 [Contact Dermatitis 22(5) , 262-6, (1990)] |