HIV diversity and drug resistance from plasma and non-plasma analytes in a large treatment programme in western Kenya.
Rami Kantor, Allison DeLong, Maya Balamane, Leeann Schreier, Robert M Lloyd, Wilfred Injera, Lydia Kamle, Fidelis Mambo, Sarah Muyonga, David Katzenstein, Joseph Hogan, Nathan Buziba, Lameck Diero
文献索引:J. Int. AIDS Soc. 17 , 19262, (2014)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Antiretroviral resistance leads to treatment failure and resistance transmission. Resistance data in western Kenya are limited. Collection of non-plasma analytes may provide additional resistance information.We assessed HIV diversity using the REGA tool, transmitted resistance by the WHO mutation list and acquired resistance upon first-line failure by the IAS-USA mutation list, at the Academic Model Providing Access to Healthcare (AMPATH), a major treatment programme in western Kenya. Plasma and four non-plasma analytes, dried blood-spots (DBS), dried plasma-spots (DPS), ViveST(TM)-plasma (STP) and ViveST-blood (STB), were compared to identify diversity and evaluate sequence concordance.Among 122 patients, 62 were treatment-naïve and 60 treatment-experienced; 61% were female, median age 35 years, median CD4 182 cells/µL, median viral-load 4.6 log10 copies/mL. One hundred and ninety-six sequences were available for 107/122 (88%) patients, 58/62 (94%) treatment-naïve and 49/60 (82%) treated; 100/122 (82%) plasma, 37/78 (47%) attempted DBS, 16/45 (36%) attempted DPS, 14/44 (32%) attempted STP from fresh plasma and 23/34 (68%) from frozen plasma, and 5/42 (12%) attempted STB. Plasma and DBS genotyping success increased at higher VL and shorter shipment-to-genotyping time. Main subtypes were A (62%), D (15%) and C (6%). Transmitted resistance was found in 1.8% of plasma sequences, and 7% combining analytes. Plasma resistance mutations were identified in 91% of treated patients, 76% NRTI, 91% NNRTI; 76% dual-class; 60% with intermediate-high predicted resistance to future treatment options; with novel mutation co-occurrence patterns. Nearly 88% of plasma mutations were identified in DBS, 89% in DPS and 94% in STP. Of 23 discordant mutations, 92% in plasma and 60% in non-plasma analytes were mixtures. Mean whole-sequence discordance from frozen plasma reference was 1.1% for plasma-DBS, 1.2% plasma-DPS, 2.0% plasma-STP and 2.3% plasma-STB. Of 23 plasma-STP discordances, one mutation was identified in plasma and 22 in STP (p<0.05). Discordance was inversely significantly related to VL for DBS.In a large treatment programme in western Kenya, we report high HIV-1 subtype diversity; low plasma transmitted resistance, increasing when multiple analytes were combined; and high-acquired resistance with unique mutation patterns. Resistance surveillance may be augmented by using non-plasma analytes for lower-cost genotyping in resource-limited settings.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
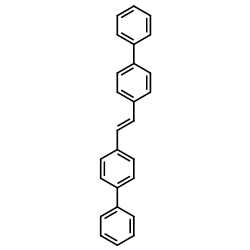 |
反式-4,4ˊ-二苯基芪
CAS:2039-68-1 |
C26H20 |
|
Quantitation of 5-Methyltetrahydrofolic Acid in Dried Blood ...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0143639, (2015)] |
|
Development and validation of a HPLC-UV method for the quant...
2015-02-01 [Clin. Chem. Lab Med. 53(3) , 435-44, (2015)] |
|
Simultaneous determination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxaz...
2015-01-01 [Bioanalysis 7 , 1137-49, (2015)] |
|
Sodium montmorillonite/amine-containing drugs complexes: new...
2015-01-01 [PLoS ONE 10 , e0121110, (2015)] |
|
Comparison of the properties of periphyton attached to modif...
2016-02-01 [Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 23 , 3718-26, (2016)] |