Oral insulin delivery using P(MAA-g-EG) hydrogels: effects of network morphology on insulin delivery characteristics.
Koji Nakamura, Robert J Murray, Jeffrey I Joseph, Nicholas A Peppas, Mariko Morishita, Anthony M Lowman
文献索引:J. Control. Release 95(3) , 589-99, (2004)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Hydrogels of poly(methacrylic acid-g-ethylene glycol) were prepared using different reaction water contents in order to vary the network mesh size, swelling behavior and insulin loading/release kinetics. Gels prepared with greater reaction solvent contents swelled to a greater degree and had a larger network mesh size. All of the hydrogels were able to incorporate insulin and protected it from release in acidic media. At higher pH (7.4), the release rates increased with reaction solvent content. Using a closed loop animal model, all of the insulin loaded formulations produced significant insulin absorption in the upper small intestine combined with hypoglycemic effects. In these studies, bioavailabilities ranged from 4.6% to 7.2% and were dependent on reaction solvent content.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
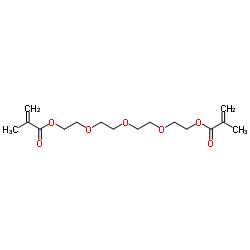 |
四乙二醇二甲基丙烯酸酯
CAS:109-17-1 |
C16H26O7 |
|
Polymeric nanocarriers for siRNA delivery to murine macropha...
2014-08-01 [Macromol. Biosci. 14(8) , 1096-105, (2014)] |
|
Construction of monomer-free, highly crosslinked, water-comp...
2014-12-01 [J. Dent. Res. 93(12) , 1326-31, (2014)] |
|
Polymethacrylate monolithic columns for hydrophilic interact...
2015-07-10 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1402 , 82-93, (2015)] |
|
Complexation Hydrogels as Oral Delivery Vehicles of Therapeu...
2015-11-01 [Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54 , 10197-10205, (2015)] |
|
pH-responsive scaffolds generate a pro-healing response.
2015-07-01 [Biomaterials 57 , 22-32, (2015)] |