The efficacy of azithromycin in the treatment of acute infraorbital space infection.
Fouad A Al-Belasy, Ashraf R Hairam
文献索引:J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 61(3) , 310-6, (2003)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
In this study, we aimed to evaluate the role of azithromycin in the treatment of acute infraorbital space infection.Sixty patients (39 men and 21 women; age range, 18 to 47 years) who had acute infraorbital space infection with pain, swelling, and general malaise were included in the study. After initial surgical therapy, patients were randomly allocated to receive either 500 mg azithromycin once daily for 3 days, 250 mg erythromycin stearate every 6 hours for 3 days, or no antibiotic. Patients were assessed at the time of admission and after 1, 2, 3, and 7 days. Pain, swelling, cervical lymphadenopathy, and sublingual temperature were assessed at each visit. Data were collected, and all groups were compared for differences in pain and swelling using the Mann-Whitney U test and for differences in lymphadenopathy and sublingual temperature using Fisher's exact test.At the time of admission, no 2 groups were statistically different at the.05 level in relation to age, gender, and presenting clinical signs or symptoms. At days 2 and 3, patients who received azithromycin had a significant reduction in pain (P =.002 and P =.02, respectively) and swelling (P =.001 and P =.013, respectively) compared with those who received no antibiotic. At day 3, patients who received erythromycin had a significant reduction in pain (P =.03) and swelling (P =.046) compared with those who received no antibiotic. In a comparison of the patients who received azithromycin with those who received erythromycin, there was no significant difference (P >.05) in the reduction of pain at any time of the study. However, at day 2, patients who received azithromycin had a significantly greater reduction in swelling (P =.002) than those who received erythromycin. In relation to the percentage of the patients with cervical lymphadenopathy and raised sublingual temperature (>37.2 degrees C), no 2 groups were statistically different at any time of the study. After 3 days of treatment, patients who received the antibiotics were clinically improved, and all patients (n = 60 patients) reviewed after 7 days had resolution of their clinical signs and symptoms.This study emphasizes the importance of surgical drainage and proves that both azithromycin and erythromycin are effective adjunctive treatments in the therapy of relatively mild odontogenic orofacial infections.Copyright 2003 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:310-316, 2003
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
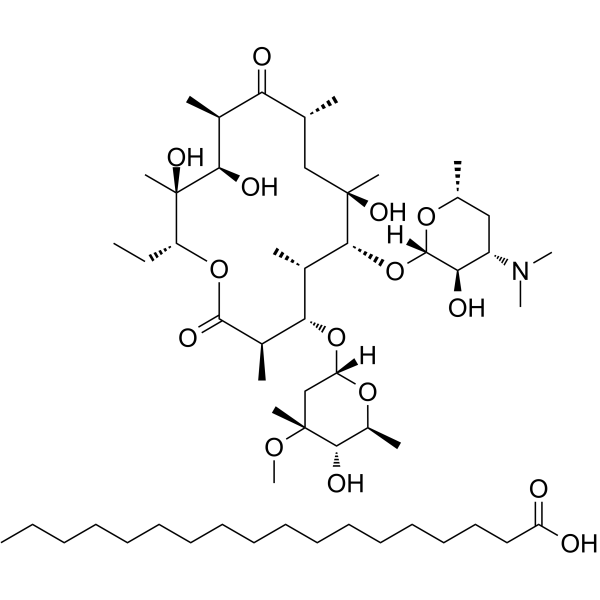 |
硬脂酸红霉素
CAS:643-22-1 |
C55H103NO15 |
|
Antibiotics for ureaplasma in the vagina in pregnancy.
2011-01-01 [Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. (9) , CD003767, (2011)] |
|
Cholestasis and liver cell damage due to hypersensitivity to...
1999-01-29 [Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 111(2) , 76-7, (1999)] |
|
Efficacy and tolerance of roxithromycin in comparison with e...
1992-01-01 [Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 24(2) , 219-25, (1992)] |
|
Selective spectrophotometric method for the determination of...
1996-08-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 14(11) , 1625-9, (1996)] |
|
Dental anxiety and the absorption of orally administered ery...
1995-12-01 [Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 80(6) , 660-5, (1995)] |