Osteolytic potential of triphenyl bismuth as an alternative contrast medium in acrylic bone cement.
Hu Xu, Saba Abdulghani, John Behiri, Afsie Sabokbar
文献索引:J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. Appl. Biomater. 75Bth ed.,, 64, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Radiopaque cement containing barium sulfate causes significantly more bone resorption in vivo and in vitro than radiolucent cement. The aim of this study was to investigate the osteolytic potential of an alternative radiopaque agent, triphenyl bismuth (TPB). Bone cement particles containing various concentration of TPB (15 and 25 wt %) prepared by two methods, blending and dissolution, were added to monocytes in a bone resorption assay and the extent of lacunar resorption on dentine slices was determined. The results clearly show that cement particles containing TPB cause less bone resorption than cement particles containing barium sulfate. In addition, our results suggest that TPB prepared by dissolution in bone cement induces less osteolytic response than TPB-cement prepared by blending. The osteolysis in response to bone cement wear particles may therefore be reduced with TPB prepared using the blending technique.(c) 2005 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. J Biomed Mater Res Part B: Appl Biomater, 2005.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
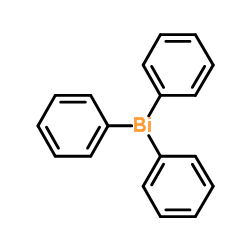 |
三苯基铋
CAS:603-33-8 |
C18H15Bi |
|
Correlation of changes in the mandible and retina/choroid va...
2015-09-01 [J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 43 , 1144-50, (2015)] |
|
Cytotoxic effects of triphenylbismuth on rat thymocytes: com...
2002-10-01 [Environ. Toxicol. 17(5) , 472-7, (2002)] |
|
Relativistic effects in triphenylbismuth and their influence...
2012-11-28 [Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(44) , 15520-4, (2012)] |
|
Development of a radiopaque, autopolymerizing dental acrylic...
1994-12-01 [J. Prosthodont. 3(4) , 213-8, (1994)] |
|
The effect of triphenylbismuth on the radiopacity and perfor...
2000-03-01 [J. Prosthodont. 9(1) , 23-9, (2000)] |