| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
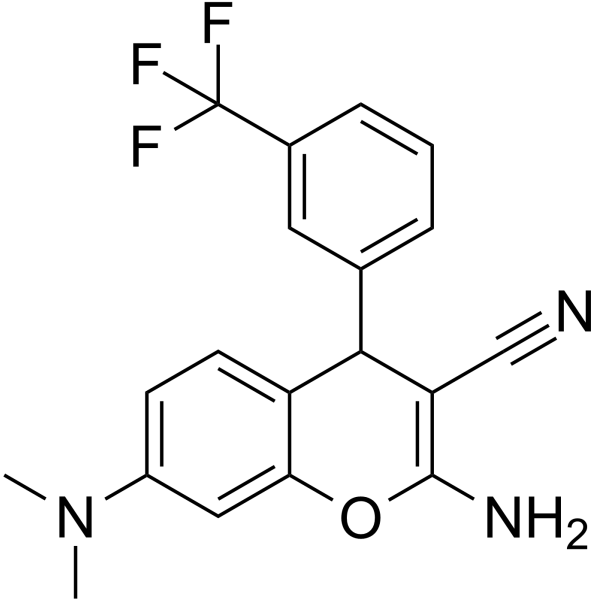 |
2-氨基-3-氰基-7-二甲基氨基-4-(3-三氟甲基苯基)-4H 苯并吡喃
CAS:331859-86-0 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
2-氨基-3-氰基-7-二甲基氨基-4-(3-三氟甲基苯基)-4H 苯并吡喃
CAS:331859-86-0 |