Prodrugs to enhance central nervous system effects of the TRH-like peptide pGlu-Glu-Pro-NH2.
Katalin Prokai-Tatrai, Vien Nguyen, Alevtina D Zharikova, April C Braddy, Stanley M Stevens, Laszlo Prokai
文献索引:Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 13(6) , 1011-4, (2003)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Potential prodrugs for the TRH-like tripeptide pGlu-Glu-Pro-NH(2) were synthesized either by esterifying the Glu side-chain of the parent peptide in solution with alcohols in the presence of resin-bound dicyclohexylcarbodiimide or by solid-phase peptide chemistry. Affinities of these ester prodrugs to lipid membranes as predictors of the transport across the blood-brain barrier were compared by immobilized artificial membrane chromatography, and prodrug activation was tested in the brain tissue of experimental animals. Esters of pGlu-Glu-Pro-NH(2) with long-chain primary alcohols emerged as potentially useful prodrugs to improve the central nervous system activity of pGlu-Glu-Pro-NH(2) upon systemic administration, as revealed by the enhancement of analeptic activity in mice.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
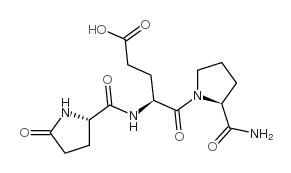 |
GLP-GLU-PRO-NH2: GLP-EP-NH2
CAS:85541-78-2 |
C15H22N4O6 |
|
Fertilization promoting peptide--a possible regulator of spe...
2001-01-01 [Vitam. Horm. 63 , 1-28, (2001)] |
|
Fertilization promoting peptide and adenosine, acting as fir...
2000-12-01 [Mol. Reprod. Dev. 57(4) , 384-92, (2000)] |
|
In vitro neuroprotection against glutamate-induced toxicity ...
2001-12-01 [Peptides 22(12) , 2091-7, (2001)] |
|
Molecular characterization of the TCP11 gene which is the hu...
2002-01-01 [Mol. Hum. Reprod. 8(1) , 24-31, (2002)] |
|
Substrate specificity of glutaminyl cyclases from plants and...
2003-12-01 [Biol. Chem. 384(12) , 1583-92, (2003)] |