A novel system combining biocatalytic dephosphorylation of L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate and electrochemical oxidation of resulting ascorbic acid.
Takashi Kuwahara, Toshimasa Homma, Mizuki Kondo, Masato Shimomura
文献索引:Biosens. Bioelectron. 26 , 3382-3385, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
An enzyme electrode was prepared with acid phosphatase (ACP) for development of a new electric power generation system using ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (AA2P) as a fuel. The properties of the electrode were investigated with respect to biocatalytic dephosphorylation of AA2P and electrochemical oxidation of resulting ascorbic acid (AA). The enzyme electrode was fabricated by immobilization of ACP through amide linkage onto a self-assembled monolayer of 3-mercaptopropionic acid on a gold electrode. AA2P was not oxidized on a bare gold electrode in the potential sweep range from -0.1 to +0.5 V vs. Ag/AgCl. However, the enzyme electrode gave an oxidation current in citric buffer solution of pH 5 containing 10 mM of AA2P. The oxidation current began to increase at +0.2V, and reached to 5.0 μA cm(-2) at +0.5 V. The potential +0.2 V corresponded to the onset of oxidation of ascorbic acid (AA). These results suggest that the oxidation current observed with the enzyme electrode is due to AA resulting from dephosphorylation of AA2P. The oxidation current increased with increasing concentration of AA2P and almost leveled off at around the concentration of 5mM. Thus the enzyme electrode brought about biocatalytic conversion of AA2P to AA, followed by electrochemical oxidation of the AA. The oxidation current is likely to be controlled by the biocatalytic reaction.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
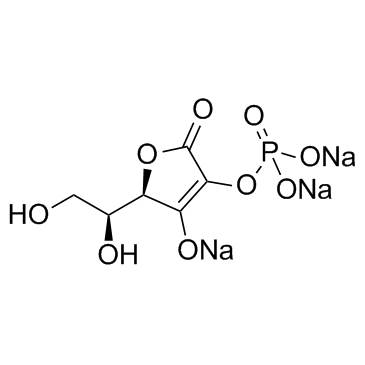 |
维生素C磷酸酯钠
CAS:66170-10-3 |
C6H6Na3O9P |
|
High-sensitive electrochemical detection of point mutation b...
2011-03-15 [Biosens. Bioelectron. 26 , 3187-3191, (2011)] |
|
Design of experiments approach to engineer cell-secreted mat...
2011-04-01 [Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39 , 1174-1185, (2011)] |
|
Modulating and modeling aggregation of cell-seeded microcarr...
2010-11-01 [J. Biotechnol. 150 , 438-446, (2010)] |
|
L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate represses the dihydrotestosteron...
2010-12-01 [Exp. Dermatol. 19 , 1110-1112, (2010)] |