Octyl methoxycinnamate modulates gene expression and prevents cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer formation but not oxidative DNA damage in UV-exposed human cell lines.
Nur Duale, Ann-Karin Olsen, Terje Christensen, Shamas T Butt, Gunnar Brunborg
文献索引:Toxicol. Sci. 114(2) , 272-284, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Octyl methoxycinnamate (OMC) is one of the most widely used sunscreen ingredients. To analyze biological effects of OMC, an in vitro approach was used implying ultraviolet (UV) exposure of two human cell lines, a primary skin fibroblast (GM00498) and a breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines. End points include cell viability assessment, assay of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and oxidated DNA lesions using alkaline elution and lesion-specific enzymes, and gene expression analysis of a panel of 17 DNA damage-responsive genes. We observed that OMC provided protection against CPDs, and the degree of protection correlated with the OMC-mediated reduction in UV dose. No such protection was found with respect to oxidative DNA lesions. Upon UV exposure in the presence of OMC, the gene expression studies showed significant differential changes in some of the genes studied and the expression of p53 protein was also changed. For some genes, the change in expression seemed to be delayed in time by OMC. The experimental approach applied in this study, using a panel of 17 genes in an in vitro cellular system together with genotoxicity assays, may be useful in the initial screening of active ingredients in sunscreens.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
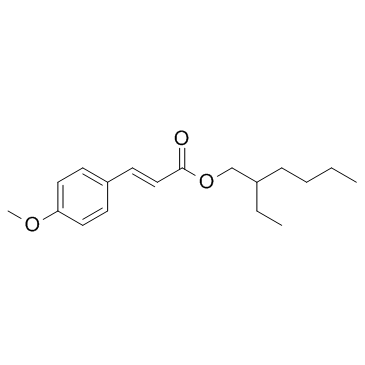 |
对甲氧基肉桂酸辛酯
CAS:5466-77-3 |
C18H26O3 |
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety ...
2011-12-01 [J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006)] |
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the predicti...
2010-07-19 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010)] |
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-indu...
2010-12-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010)] |
|
Atmospheric pressure gas chromatography-time-of-flight-mass ...
2014-12-03 [Anal. Chim. Acta 851 , 1-13, (2014)] |
|
Growth of cedar-like Au nanoparticles coating on an etched s...
2015-05-30 [Anal. Chim. Acta 876 , 55-62, (2015)] |