Impairment of synaptic vesicle exocytosis and recycling during neuromuscular weakness produced in mice by 2,4-dithiobiuret.
You-Fen Xu, Dawn Autio, Mary B Rheuben, William D Atchison
文献索引:J. Neurophysiol. 88(6) , 3243-58, (2002)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Chronic treatment of rodents with 2,4-dithiobiuret (DTB) induces a neuromuscular syndrome of flaccid muscle weakness that mimics signs seen in several human neuromuscular disorders such as congenital myasthenic syndromes, botulism, and neuroaxonal dystrophy. DTB-induced muscle weakness results from a reduction of acetylcholine (ACh) release by mechanisms that are not yet clear. The objective of this study was to determine if altered release of ACh during DTB-induced muscle weakness was due to impairments of synaptic vesicle exocytosis, endocytosis, or internal vesicular processing. We examined motor nerve terminals in the triangularis sterni muscles of DTB-treated mice at the onset of muscle weakness. Uptake of FM1-43, a fluorescent marker for endocytosis, was reduced to approximately 60% of normal after either high-frequency nerve stimulation or K(+) depolarization. Terminals ranged from those with nearly normal fluorescence ("bright terminals") to terminals that were poorly labeled ("dim terminals"). Ultrastructurally, the number of synaptic vesicles that were labeled with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) was also reduced by DTB to approximately 60%; labeling among terminals was similarly variable. A subset of DTB-treated terminals having abnormal tubulovesicular profiles in their centers did not respond to stimulation with increased uptake of HRP and may correspond to dim terminals. Two findings suggest that posttetanic "slow endocytosis" remained qualitatively normal: the rate of this type of endocytosis as measured with FM1-43 did not differ from normal, and HRP was observed in organelles associated with this pathway- coated vesicles, cisternae, as well as synaptic vesicles but not in the tubulovesicular profiles. In DTB-treated bright terminals, end-plate potential (EPP) amplitudes were decreased, and synaptic depression in response to 15-Hz stimulation was increased compared with those of untreated mice; in dim terminals, EPPs were not observed during block with D-tubocurarine. Nerve-stimulation-induced unloading of FM1-43 was slower and less complete than normal in bright terminals, did not occur in dim terminals, and was not enhanced by alpha-latrotoxin. Collectively, these results indicate that the size of the recycling vesicle pool is reduced in nerve terminals during DTB-induced muscle weakness. The mechanisms by which this reduction occurs are not certain, but accumulated evidence suggests that they may include defects in either or both exocytosis and internal vesicular processing.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
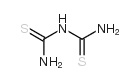 |
二硫代缩二脲
CAS:541-53-7 |
C2H5N3S2 |
|
Temporal analysis of dithiobiuret neurotoxicity in rats and ...
1987-11-01 [Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 91(2) , 212-21, (1987)] |
|
Voltage clamp analysis reveals multiple populations of quant...
1991-01-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 256(1) , 159-63, (1991)] |
|
Differential effects of 2,4-dithiobiuret on the synthesis an...
1995-12-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 275(3) , 1453-62, (1995)] |
|
Morphometric characterization of the neuromuscular junction ...
2004-04-15 [Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 196(2) , 266-86, (2004)] |
|
2,4-Dithiobiuret in rats: cognitive facilitation after acute...
1996-02-01 [Psychopharmacology 123(3) , 267-79, (1996)] |