Characterization of aliphatic hydrocarbons in deep subsurface soils near the outskirts of Beijing, China.
You-Feng Zhu, Hui Liu, Zhi-Qun Xi, Hang-Xin Cheng, Xiao-Bai Xu
文献索引:J. Environ. Sci. (China) 17(3) , 360-4, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Thirty-nine deep subsurface soils (150-180 cm depth) near the outskirts of Beijing were investagated. The concentrations including n-alkanes from C13 to C36, pristane and phytane were in the range of 0.60 to 170.10 microg/g, with a median value of 4.26. Carbon preference index values for n-alkanes ranged from 1.08 to 2.98, with a median value of 1.48. The percentage contribution of "wax" n-alkanes was in the range of 6.03%--46.22%. A predominance of odd/even carbon n-alkanes and unresolved complex mixtures with different shapes and ranges were frequently observed. Factor analysis reduced the data set into three principal components and confirming contributions from low (19.58%), medium (20.49%) molecular weight species and long-chain n-alkanes (43.41%), respectively. Molecular biomarkers such as pristane, phytane, hopanes and steranes were detected. Based on the principal component analysis, the concentration profiles and molecular markers, it was found that the aliphatic hydrocarbons were from both biogenic and anthropogenic sources.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
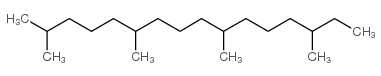 |
植烷
CAS:638-36-8 |
C20H42 |
|
Chemical constituents of Heteroplexis micocephala.
2009-06-01 [J. Nat. Prod. 72 , 1184-90, (2009)] |
|
Production of pristane and phytane in the marine environment...
2011-11-01 [Res. Microbiol. 162(9) , 923-33, (2011)] |
|
Determination of anthropogenic and biogenic compounds on atm...
2010-01-01 [Sci. Total Environ. 408(23) , 5836-44, (2010)] |
|
Cluster of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) associated wit...
2007-01-01 [Environ. Health 6 , 8, (2007)] |
|
Isotopic biogeochemistry of the Oxford Clay Formation (Juras...
1994-01-01 [J. Geol. Soc. London. 151 , 139-52, (1994)] |