HME--a novel derivative for direct iodination in steroid radioimmunoassays.
R Stupnicki, T Kowalczyk-Przeewłoka, E Kula, L Y Kasongo
文献索引:J. Steroid Biochem. 28(6) , 663-7, (1987)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Steroid derivatives containing histidine methyl ester (HME), instead of histamine, were prepared by mixed anhydride coupling. The derivatives were crystalline, and when labelled in microgram quantities by using Iodo-gen (exposure time 1 h) the yield of the immunoreactive fraction was 40-50%. The products were similar in immunoreactivity and stability to the known histamine derivatives. Assay parameters obtained with HME-derivatives were compared with those obtained with tritiated steroids and with analogous TME-derivatives. A heterologous assay of progesterone (3 antisera against 12 alpha-succinyl-BSA, and methylsuccinyl derivatives for labelling substituted at 11 alpha-position), and a homologous assay of cortisol (4 antisera against 21-succinyl-BSA, and 21-carbonyl-derivatives for labelling) were studied. The HME-derivatives produced logit-log curves with slopes comparable to those in tritium-based assays. The sensitivity, as expressed by ED50 values, was by 66% higher than in tritium assays, and by 50% higher than for the tyramine derivative in a similar heterologous assay. The HME-based assay for cortisol was by 26% less sensitive compared to tritium, but several times more sensitive than in case of analogous TME-based assay.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
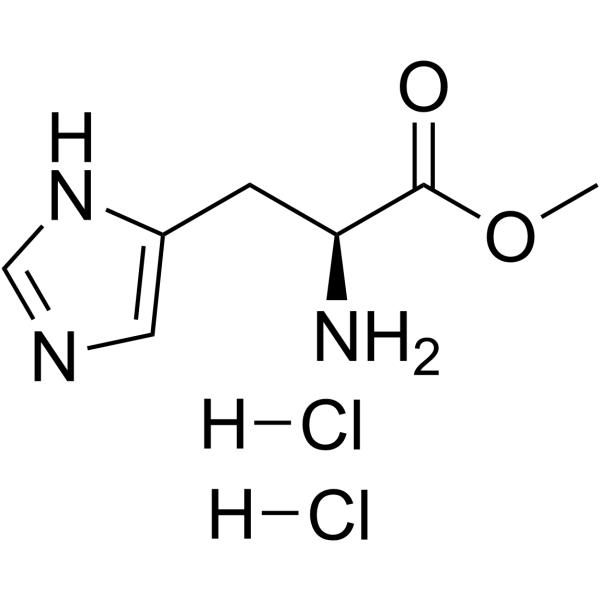 |
L-组氨酸甲酯二盐酸盐
CAS:7389-87-9 |
C7H13Cl2N3O2 |
|
Preparation and use of poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) cryog...
2013-02-01 [J. Food Sci. 78(2) , E238-43, (2013)] |
|
A proximal pair of positive charges provides the dominant li...
2012-04-01 [Biochem. J. 443(1) , 65-73, (2012)] |
|
The biological activity of hydrogen peroxide. IV. Enhancemen...
1988-03-01 [Mutat. Res. 198(1) , 233-40, (1988)] |
|
Carbonic anhydrase activators: gold nanoparticles coated wit...
2011-03-10 [J. Med. Chem. 54(5) , 1170-7, (2011)] |
|
Gas-phase structure of protonated histidine and histidine me...
2005-09-22 [J. Phys. Chem. A 109(37) , 8329-35, (2005)] |