Production of cloned mice from somatic cells, ES cells, and frozen bodies.
Sayaka Wakayama, Eiji Mizutani, Teruhiko Wakayama
文献索引:Meth. Enzymol. 476 , 151-69, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) has become a unique and powerful tool for epigenetic reprogramming research and gene manipulation in animals. Although the success rates of somatic cloning have been inefficient and the mechanism of reprogramming is still largely unknown, therefore, the nuclear transfer (NT) method has been thought of as a "black box approach" and inadequate to determine the detail of how genomic reprogramming occurs. However, only the NT approach can reveal dynamic and global modifications in the epigenome without using genetic modification, as well as can create live animals. At present, this is the only technique available for the preservation and propagation of valuable genetic resources from mutant mice that are infertile or too old, or recovered from carcasses, without the use of germ cells. This chapter describes a basic protocol for mouse cloning and embryonic stem (ES) cell establishment from cloned embryo using a piezo-actuated micromanipulator. This technique will greatly help not only in mouse cloning but also in other forms of micromanipulation such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) into oocytes or ES cell injection into blastocysts. In addition, we describe a new, more efficient mouse cloning protocol using histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi), which increases the success rates of cloned mice or establish rate of ES cells to fivefold.Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
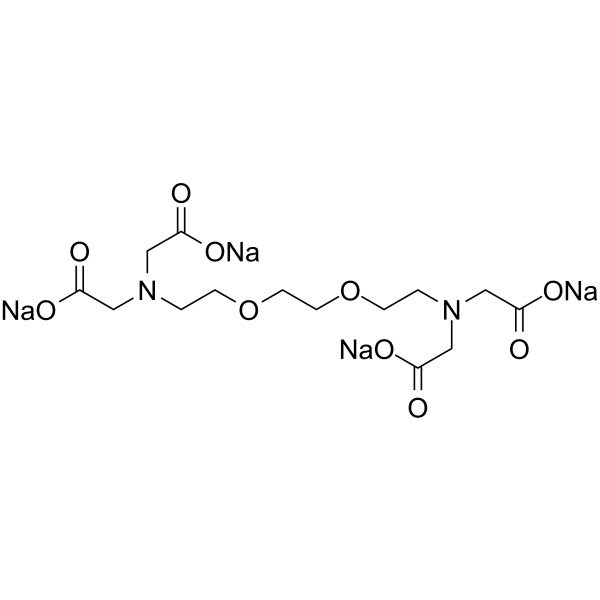 |
乙二醇-双(β-氨乙醚)-N,N,N′,N′-四乙酸 四钠盐
CAS:13368-13-3 |
C14H20N2Na4O10 |
|
PAR-CLIP (Photoactivatable Ribonucleoside-Enhanced Crosslink...
2014-01-01 [Meth. Enzymol. 539 , 113-61, (2014)] |
|
Using somatic-cell nuclear transfer to study aging.
2013-01-01 [Methods Mol. Biol. 1048 , 109-26, (2013)] |
|
Cloning of ES cells and mice by nuclear transfer.
2009-01-01 [Methods Mol. Biol. 530 , 251-65, (2009)] |
|
Shirley P and Saunders T L
[Advanced Protocols For Animal Transgenesis , (2011), 271-277] |
|
Schmid, R.W., Reilly, C.N.
[Anal. Chem. 29 , 264, (1957)] |