Effects of quinestrol on reproductive hormone expression, secretion, and receptor levels in female Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus).
Xiaohui Lv, Y Guo, D Shi
文献索引:Theriogenology 77(6) , 1223-31, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Quinestrol, a synthetic estrogen with marked estrogenic effects and prolonged activity, has potential as a contraceptive for Mongolian gerbils. The objective of this study was to describe the effects of quinestrol on reproductive hormone expression, secretion, and receptor levels in female Mongolian gerbils. Serum and pituitary concentrations of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) were decreased, whereas serum concentrations of estradiol (E2) and progesterone (P4) were increased after quinestrol treatment; the effects were both time- and dose-dependent. Furthermore, quinestrol downregulated expression of FSHβ and LHβ mRNA in the pituitary gland, as well as FSH receptor (FSHR) and estrogen receptor (ER) β in the ovary. However, it up-regulated mRNA expression levels of ERα and progesterone receptor (PR) in the pituitary gland and uterus, as well as mRNA for LH receptor (LHR) and PR in the ovary (these effects were time- and dose-dependent). In contrast, quinestrol had no significant effects on the mRNA expression levels of ERα in the ovary, or the gonadotropin α (GtHα) subunit in the pituitary gland. We inferred that quinestrol impaired synthesis and secretion of FSH and LH and that the predominant ER subtype in the pituitary gland of Mongolian gerbils may be ERα. Overall, quinestrol disrupted reproductive hormone receptor expression at the mRNA level in the pituitary-gonadal axis of the Mongolian gerbil.Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
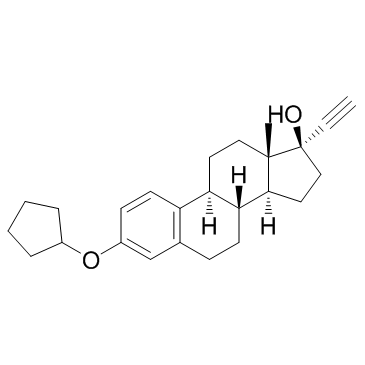 |
炔雌醇环戊醚
CAS:152-43-2 |
C25H32O2 |
|
The bioaccumulation and biotransformation of synthetic estro...
2014-10-01 [Aquat. Toxicol. 155 , 84-90, (2014)] |
|
Photodegradation of quinestrol in waters and the transformat...
2012-11-01 [Chemosphere 89(11) , 1419-25, (2012)] |
|
Quinestrol treatment induced testicular damage via oxidative...
2011-01-01 [Exp. Anim. 60(5) , 445-53, (2011)] |
|
Behavioral evaluation of quinestrol as a sterilant in male B...
2011-10-24 [Physiol. Behav. 104(5) , 1024-30, (2011)] |
|
Subfertile effects of quinestrol and levonorgestrel in male ...
2012-01-01 [Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 24(2) , 297-308, (2012)] |