Targeted gap junction protein constructs reveal connexin-specific differences in oligomerization.
Jayasri Das Sarma, Fushan Wang, Michael Koval
文献索引:J. Biol. Chem. 277(23) , 20911-8, (2002)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
To define further the mechanisms of gap junction protein (connexin (Cx)) oligomerization without pharmacologic disruption, we have examined the transport and assembly of connexin constructs containing C-terminal di-lysine-based endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (HKKSL) or ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (AKKFF) targeting sequences. By immunofluorescence microscopy, Cx43-HKKSL transiently transfected into HeLa cells showed a predominantly ER localization, although Cx43-AKKFF was localized to the perinuclear region of the cell. Sucrose gradient analysis of Triton X-100-solubilized connexins showed that either Cx43-HKKSL or Cx43-AKKFF expressed alone by HeLa cells was maintained as an apparent monomer. In contrast to Cx43-HKKSL, Cx32-HKKSL was maintained in the ER as stable hexamers, consistent with the notion that Cx32 and Cx43 oligomerization occur in distinct intracellular compartments. Furthermore, Cx43-HKKSL and Cx43-AKKFF inhibited trafficking of Cx43 and Cx46 to the plasma membrane. The inhibitory effect was because of the formation of mixed oligomers between Cx43-HKKSL or Cx43-AKKF and wild type Cx43 or Cx46. Taken together, these results suggest that Cx43-HKKSL and Cx43-AKKFF recirculate through compartments where oligomerization occurs and may be maintained as apparent monomers by a putative Cx43-specific quality control mechanism.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
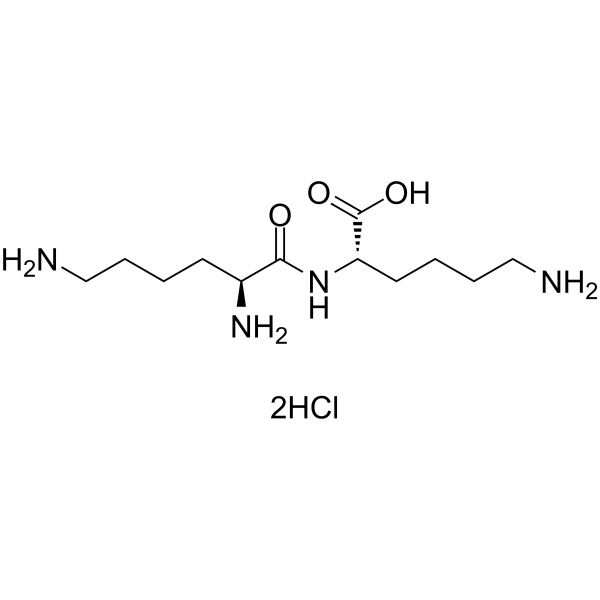 |
L-赖氨酰-L-赖氨酸二盐酸盐
CAS:52123-30-5 |
C12H28Cl2N4O3 |
|
Canine zona pellucida glycoprotein-3: up-scaled production, ...
2015-01-01 [Vaccine 33(1) , 133-40, (2014)] |
|
A single binding site for dilysine retrieval motifs and p23 ...
1998-09-29 [Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95(20) , 11649-54, (1998)] |
|
Intracellular targeting signals contribute to localization o...
2004-06-01 [J. Virol. 78(11) , 5913-22, (2004)] |
|
Peptide binding in OppA, the crystal structures of the perip...
1997-08-12 [Biochemistry 36(32) , 9747-58, (1997)] |
|
Endoplasmic reticulum retention of the large splice variant ...
2005-10-01 [Glycobiology 15(10) , 905-11, (2005)] |