Impact of combined oral contraceptives containing ethinylestradiol on the liver microsomal metabolism.
Krzysztof Jonderko, Piotr Skałba, Anna Kasicka-Jonderko, Magdalena Kamińska, Dorota Bizior-Frymus, Renata Dyja
文献索引:Eur. J. Contracept. Reprod. Health Care 18(4) , 284-92, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
To check whether currently used combined oral contraceptives (COCs) containing ethinylestradiol (EE) affect the liver microsomal metabolism.(13)C-methacetin breath test ((13)C-MBT) - a sensitive non-invasive probe of cytochrome P-450 1A2 activity - was performed in 15 women on day 14, 15, 16, 17 or 18 of intake of their COC (containing EE), and between day 1 and 5 during the withdrawal bleeding, as well as in nine women not using hormonal contraception during the luteal phase of their cycle (between the 17th and the 23rd day), and between day 1 and 5 during menstruation.The maximum breath (13)C elimination was significantly lower during the phase of intake of contraceptive pills than during withdrawal bleeding: 31.5 ± 2.2 %/h vs. 38.2 ± 1.9 %/h (p = 0.0045), whereas the time to reach it was similar on the two study days: 21.2 ± 1.2 min vs. 21.0 ± 1.1 min. Between the 27th and the 180th min of observation the cumulative breath (13)C elimination was statistically significantly lower during intake of the pill than during withdrawal bleeding. No significant menstrual cycle phase-dependent fluctuations in the results of the (13)C- methacetin breath test were observed in the control group.COCs containing EE markedly inhibit hepatic microsomal function. This phenomenon must be taken into consideration when interpreting results of (13)C-MBT.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
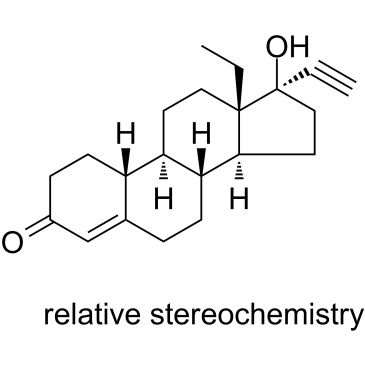 |
炔诺孕酮
CAS:6533-00-2 |
C21H28O2 |
|
Progestagen-only oral contraceptives: a preliminary report o...
1973-01-01 [Drugs 6(3) , 169-81, (1973)] |
|
Types of combined oral contraceptives used by US women.
2012-12-01 [Contraception 86(6) , 659-65, (2012)] |
|
Newer non-oral hormonal contraception.
2013-01-01 [BMJ 346 , f341, (2013)] |
|
Antimüllerian hormone levels decrease in women using combine...
2013-04-01 [Fertil. Steril. 99(5) , 1305-10, (2013)] |
|
Recent combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) and the risk ...
2013-01-01 [Contraception 87(1) , 93-100, (2013)] |