Different action of memantine and caroverine on glutamatergic transmission in the mammalian cochlea.
Elmar Oestreicher, Klaus Ehrenberger, Dominik Felix
文献索引:Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 59 , 18-25, (2002)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Glutamate is the major transmitter candidate between inner hair cells and the afferent neurons of the mammalian cochlea. We investigated the action of memantine (1-amino-3,5-dimethyl-adamantane) and the quinoxaline derivative caroverine [1-diethylaminoethyl-3,8-(p-methoxybenzyl)-1,2-dihydro-quinoxaline-dione] on the glutamatergic transmission in the guinea pig cochlea utilizing extracellular recording techniques and microiontophoretic ejection of substances. While memantine was able to inhibit the NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate)-induced firing, the AMPA (alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid)-stimulated activity was unaffected. In contrast, caroverine could block both NMDA- as well as AMPA-induced firing. As memantine and caroverine are currently in clinical use, these substances could be introduced to the treatment of several cochlear disorders.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
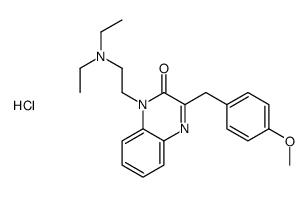 |
Caroverine hydrochloride
CAS:55750-05-5 |
C22H28ClN3O2 |
|
Possible contribution of pannexin channel to ATP-induced cur...
2011-06-07 [Brain Res. 1394 , 71-8, (2011)] |
|
[Drug therapy for disturbances of smelling].
2004-02-01 [Laryngorhinootologie. 83(2) , 124-34, (2004)] |
|
[Therapy of olfactory loss].
2003-08-01 [Laryngorhinootologie. 82(8) , 552-4, (2003)] |
|
Caroverine, a multifunctional drug with antioxidant function...
2003-01-01 [Biofactors 19(1-2) , 79-85, (2003)] |
|
Caroverine inhibits the conditioned place aversion induced b...
2003-10-02 [Neurosci. Lett. 349(2) , 91-4, (2003)] |