Diploptene: an indicator of terrigenous organic carbon in Washington coastal sediments.
F G Prahl, J M Hayes, Xie T-M
文献索引:Limnol. Oceanogr. 37(6) , 1290-300, (1992)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The pentacyclic triterpene 17 beta(H),21 beta(H)-hop-22(29)-ene (diploptene) occurs in sediments throughout the Columbia River drainage basin and off the southern coast of Washington state in concentrations comparable to long-chain plantwax n-alkanes. The same relationship is evident for diploptene and long-chain n-alkanes in soils from the Willamette Valley. Microorganisms indigenous to soils and soil erosion are indicated as the biological source and physical process, respectively, for diploptene in coastal sediments. Similarity between the stable carbon isotopic composition (delta 13CPDB) of diploptene isolated from soil in the Willamette Valley (-31.2 +/- 0.3%) and from sediments deposited throughout the Washington coastal environment (-31.2 +/- 0.5%) supports this argument. Values of delta for diploptene in river sediments are variable and 8-17% lighter, indicating that an additional biological source such as methane-oxidizing bacteria makes a significant contribution to the diploptene record in river sediments. Selective biodegradation resulting from a difference in the physicochemical association within eroded particles can explain the absence of the more-13C-depleted form of diploptene in Washington coastal sediments, but this mechanism remains unproven.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
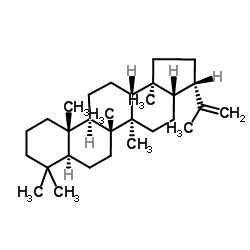 |
何帕烯
CAS:1615-91-4 |
C30H50 |
|
Profound insights into squalene cyclization.
2004-01-01 [Chem. Biol. 11(1) , 12-4, (2004)] |
|
Squalene-hopene cyclases.
2011-06-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77(12) , 3905-15, (2011)] |
|
Hopane-type triterpenes and binaphthopyrones from the scale ...
2010-04-23 [J. Nat. Prod. 73 , 688-92, (2010)] |
|
Hopanoid production by Desulfovibrio bastinii isolated from ...
2009-04-01 [FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 293(1) , 73-8, (2009)] |
|
Quantitative determination of various hopanoids in microorga...
1989-08-15 [Anal. Biochem. 181(1) , 120-4, (1989)] |